Introduction
In the complex world of electrical engineering, understanding current density and connection standards for low-voltage electrical cabinets is crucial. This comprehensive guide explores the nuanced requirements of North American electrical systems, focusing on material selection, current carrying capacity, and connection methodologies.

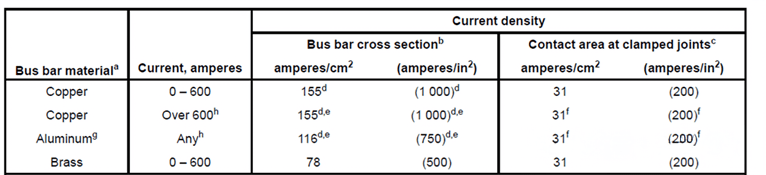
Understanding Current Density Fundamentals
Material Considerations
- Copper conductors: Maximum current density of 1.55A/mm²
- Aluminum conductors: Maximum current density of 1.16A/mm²
- Brass conductors: Maximum current density of 0.78A/mm²
Practical Calculation Examples
When designing electrical cabinets for 3000A systems:
- Copper bus bar requirements: Minimum 1935.48mm² cross-sectional area
- Aluminum bus bar requirements: Minimum 2586.20mm² cross-sectional area
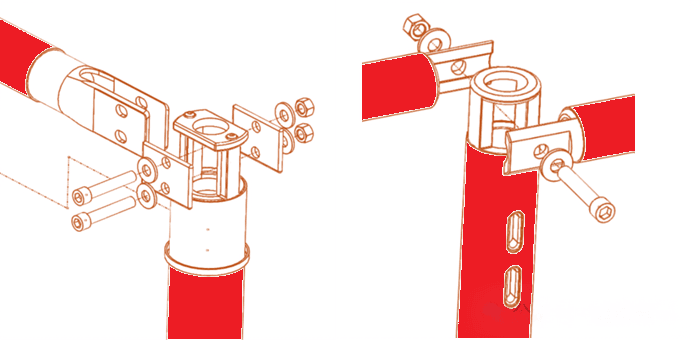
Critical Connection Standards
Key Regulatory Insights
- GB/T5273-2016 standard eliminates strict terminal dimension requirements
- Manufacturers now have flexibility in bus bar connection design
- Connection methods can be customized based on product specifications
Connection Surface Area Regulations
- No reduction allowed for bolt or rivet hole diameters
- Silver or tin-plated connectors recommended
- Minimum international annealed copper standard: 55% conductivity
Advanced Connection Principles
Current Density at Connection Points
Strict regulations mandate:
- Maximum current density of 0.31A/mm² for all conductor materials
- Connection area calculations include fastener hole spaces
Practical Implementation
- For 1200A systems, connection length must exceed 48mm
- Multiple bus bar connections require proportionally increased surface areas
Beyond Standard Compliance
Holistic System Evaluation
- Temperature rise testing supersedes strict standard adherence
- Factors like pressure, thermal conductivity, and heat dissipation critical
- Comprehensive system simulation recommended
Conclusion
Designing low-voltage electrical cabinets requires a nuanced understanding of material properties, current density, and connection standards. By balancing regulatory requirements with innovative engineering approaches, professionals can create more efficient, reliable electrical systems.
About the Expertise
This insight is brought to you by Nengfu Electrical, a Shanghai-based company specializing in comprehensive electrical system solutions, committed to driving technological innovation and sustainable development in power infrastructure.
